
Prompting Like a Pro: Crafting AI-Assisted Development Workflows
Prompt Engineering 101 LearningsThere are many ways to effectively prompt an LLM to get a good response, and the one I am sharing here is tailored for software development. These particular insights come from working with Claude Code. The tips and tricks outlined below are based on my experience and can help you improve your development workflow with LLMs—so give them a try!
Getting Started
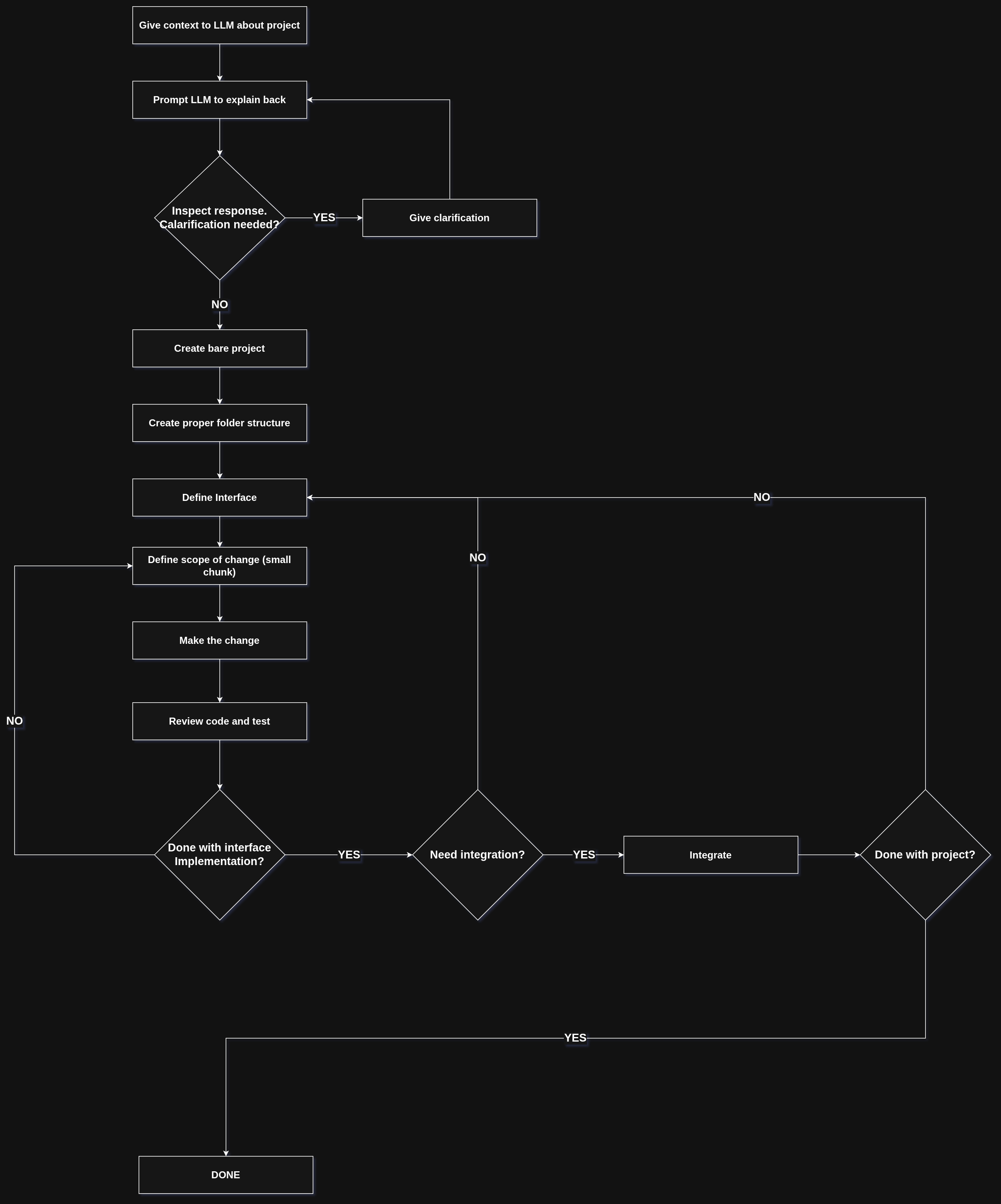
Have a clear and concise understanding of what you want to build. It is really hard to work with LLM if you don’t have clarity on what you want and how you want to build it. Once you start your project, give the LLM the context of what you want to build. It doesn’t have to be technical, you can give an overview of the project. You can then ask the LLM to explain it back so that you can review its response and correct it if there are any misunderstandings. Once you have done that, you can start the coding process.
Build the foundation first
It is important for you to first set the foundations. Ask it to create a project using the tech stack with specific versions that you want to use. Build out the folder layouts and structure the project first so that the LLM doesn’t place all the code in a single place. Once you are happy with the structure of the project you can move to the next phase.
Boundaries are good
Have clear boundaries between different areas of the code base. Create interfaces that serve a specific purpose and work through those interfaces. If you have clean interfaces to interact with different parts of the code, the LLM will be less confused and have better results during integration. It also provides a clean separation when you want to refactor the code later.
Definition
An interface is a defined boundary that specifies what functionalities are exposed and how other components can interact with them, without revealing the underlying implementation.
Examples of Interfaces
| Context | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Java Interface | UserService interface |
Defines a contract of methods that implementing classes must follow. |
| Ruby Module | Authenticatable module |
Provides a reusable set of behaviors; acts as a shared interface. |
| HTTP API | /users endpoint |
Exposes operations over HTTP; defines system-to-system interaction. |
| UI Component | UserCard component with props |
Defines what data/actions a UI component expects and emits. |
Iterate Iterate Iterate
The best way to work with LLMs is to have iteration cycles as small as possible. Build small features, test and repeat. Always focus on a single part of the code at a time and don’t make huge changes. This way you will have a much easier time reviewing the changes as well as testing. Building a large feature at once may seem faster at first but the mess it will create will slowly decrease the iteration speed.
Tips
Gamify the system
You can create a scoring system for the LLM and it will try to optimize for the highest score. You can create a virtual scoring system with points, coins, items (use your imagination). Once you have decided, stick to it. Whenever LLM gives you the response you want, give it a positive score and vice versa. This will create a reinforcement loop and then the LLM will start optimising for the positive scores, thereby giving you the good response.
LLMs are good with XML
Use XML format on prompt and use a similar format every time.
Eg:
<Observation>What happened in the last prompt</Observation>
<GoldCoins>score</GoldCoins>
<Problem>Problem you want to solve</Problem>
<Solution>How you want to solve it</Solution>
You can be as creative as you want in creating these schemas, but once you pick one, try to stick with it.
Workflow
Conclusion
Prompting an LLM effectively can dramatically improve your productivity and code quality. By providing clear context, building structured foundations, maintaining clean interfaces, and working in small iterations, you’ll unlock the full potential of AI-assisted development. Don’t be afraid to get creative—gamifying interactions or using structured formats like XML can lead to even better results. Give these techniques a try in your own workflow and see how they transform your development experience.
For further reading and inspiration, check out:
Happy building!