
Using Firebase Cloud Functions: Exporting Firestore Data to Excel in React Apps
Software Craftsmanship ReactOne day, one of my team members gave me a challenge: we needed a way to download our admin data as Excel files for better reporting. Despite searching, I couldn’t find a tutorial that fit our needs for a React/Next.js app. After more research, including using AI tools like ChatGPT, I figured out a solution. In this blog, I’ll show you how we use Firebase Cloud Functions to make it happen.
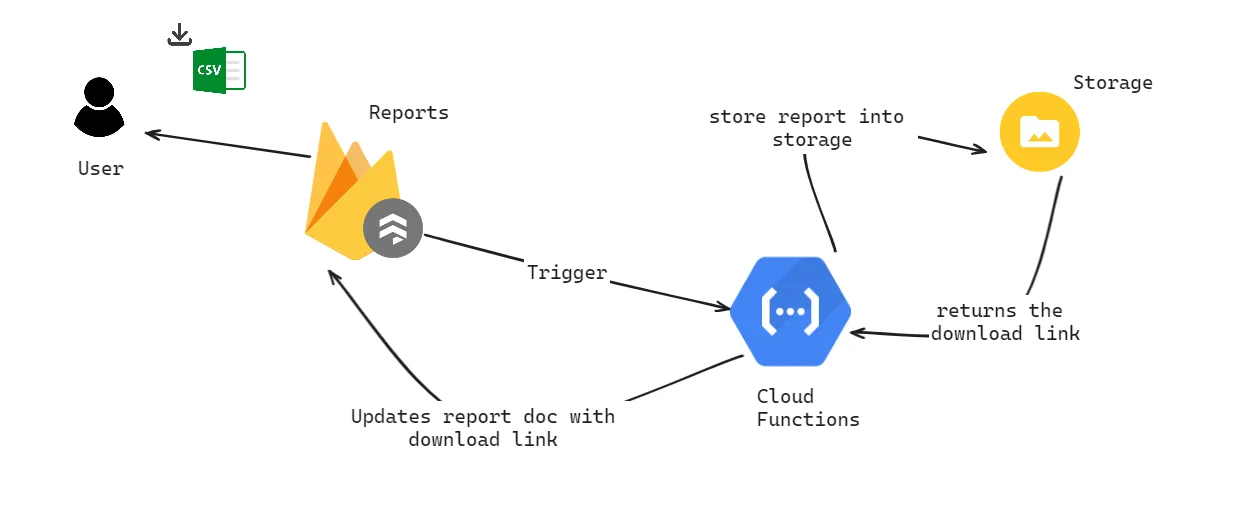
Setting up Firebase
Before we dive into the code, ensure you have a Firebase project set up with Firestore as your database. If you’re new to Firebase, follow their official documentation to create a new project and enable the Firestore database and cloud functions.
Table.jsx
Once you have your Firebase project and Firestore database ready, the next step is to integrate Firestore data into your React/Next.js application. This example illustrates how to display Firestore data in a table within a React component using hooks like useState and useEffect.
import { db } from "../utils/firebase";
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import { collection, query, orderBy, getDocs } from "firebase/firestore";
import Button from "./Button";
export default function Table() {
const [logs, setLogs] = useState([]);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
const fetchLogs = async () => {
setLoading(true);
const logsRef = collection(db, "bills");
const logsBills = query(logsRef, orderBy("time", "desc"));
const logsSnapshot = await getDocs(logsBills);
const logsData = logsSnapshot.docs.map((doc) => doc.data());
setLogs(logsData);
setLoading(false);
};
fetchLogs();
}, []);
return (
<div className=" dark:bg-slate-900 bg-gray-100 flex h-full items-left pb-96 text-black">
<div className="max-w-auto mx-auto p-6">
<div className="text-center">
<h1 className="text-3xl font-bold text-gray-800 sm:text-4xl dark:text-white">
User Bills
</h1>
</div>
<div className="flex flex-col bg-white rounded-md mt-4 p-6">
<div className="flex flex-col">
<div className="-m-1.5 overflow-x-auto">
<div className="p-1.5 min-w-full inline-block align-middle">
<div className="overflow-hidden">
<table className="min-w-full divide-y divide-gray-200 dark:divide-gray-700">
<thead>
<tr>
<th
scope="col"
className="px-2 py-3 text-center text-xs font-medium text-gray-500 uppercase"
>
Index
</th>
<th
scope="col"
className="px-2 py-3 text-center text-xs font-medium text-gray-500 uppercase"
>
Name
</th>
<th
scope="col"
className="px-2 py-3 text-center text-xs font-medium text-gray-500 uppercase"
>
Bills
</th>
<th
scope="col"
className="px-2 py-3 text-center text-xs font-medium text-gray-500 uppercase"
>
Time
</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody className="divide-y divide-gray-200 dark:divide-gray-700">
{logs.map((item, index) => (
<tr key={index}>
<td className="px-2 py-4 whitespace-nowrap text-sm font-medium text-black place-self-center">
{index + 1}
</td>
<td className="px-2 py-4 whitespace-nowrap text-center font-bold text-sm text-black">
<div className="flex flex-row gap-2 justify-center items-center">
<span>{item.name}</span>
</div>
</td>
<td className="px-2 py-4 whitespace-nowrap text-center font-bold text-sm text-black">
<div className="flex flex-row gap-2 justify-center items-center">
<span>{item.bills}</span>
</div>
</td>
<td className="px-2 py-4 whitespace-nowrap text-center text-sm font-bold">
<div className="text-black">
{item?.time
? item?.time.toDate().toLocaleTimeString() +
" " +
item?.time.toDate().toDateString()
: "Not Set"}
</div>
</td>
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
<div className="flex justify-center">
{loading && <p>Loading..</p>}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<Button />
</div>
</div>
);
}
- Here we have a very simple table showing data fetched from Firestore using React hooks.
- Additionally, there is a “Get Report” button that triggers a cloud function.
Button.jsx
This component works as a trigger for the cloud function.
import { addDoc, collection, doc, onSnapshot } from "firebase/firestore";
import { db } from "../utils/firebase";
import { useState } from "react";
const Button = () => {
const [report, setReport] = useState("");
const [reportLoaded, setReportLoaded] = useState(false);
const handleDownload = async () => {
try {
const reportsRef = collection(db, "reports");
const report = await addDoc(reportsRef, {
status: "pending",
type: "queries",
downloadLink: "",
});
const reportDocRef = doc(db, "reports", report.id);
onSnapshot(reportDocRef, (doc) => {
setReport(doc.data().downloadLink);
});
setReportLoaded(true);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};
return (
<div className="flex flex-col items-center justify-center my-4">
<button
onClick={handleDownload}
className="p-2 rounded-md text-sm bg-white text-black font-bold"
>
Get Report
</button>
{report === "" && reportLoaded ? (
<div className="flex flex-row justify-center my-4">
<div
className="animate-spin inline-block w-6 h-6 border-[3px] border-current border-t-transparent text-gray-800 rounded-full dark:text-white"
role="status"
aria-label="loading"
>
<span className="sr-only">Loading...</span>
</div>
</div>
) : report !== "" && reportLoaded ? (
<div className="bg-white mt-2 rounded-md p-2 text-sm font-extrabold text-purple-800">
<a target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer" href={report}>
Download Report
</a>
</div>
) : (
""
)}
</div>
);
};
export default Button;
- When the “Get Report” button is clicked, a document is added to the reports collection, which acts as a trigger for the cloud function.
- The
onSnapshot()method watches for any updates to the document, retrieving the download link once it’s ready.
Cloud Function
Setting up the Environment
Before diving into the code, ensure you have the necessary modules installed and initialized:
- Firebase Functions: Manage cloud functions.
- Firebase Admin: Interact with various Firebase services, including Firestore and Storage.
- Papaparse: A powerful library for parsing and un-parsing CSV files.
- date-fns (Optional): A library to manipulate JavaScript dates in a straightforward way.
/**
* Import function triggers from their respective submodules:
*
* const {onCall} = require("firebase-functions/v2/https");
* const {onDocumentWritten} = require("firebase-functions/v2/firestore");
*
* See a full list of supported triggers at https://firebase.google.com/docs/functions
*/
const functions = require("firebase-functions");
const admin = require("firebase-admin");
admin.initializeApp();
const db = admin.firestore();
const fs = require("fs-extra");
const bucket = admin.storage().bucket();
const path = require("path");
const os = require("os");
const Papa = require("papaparse");
const { format, addHours, addMinutes } = require("date-fns");
exports.createCSV = functions.region("asia-south1")
.firestore.document("reports/{reportId}")
.onCreate(async (change, context) => {
const reportId = context?.params?.reportId || "test";
const fileName = `reports/${reportId}.csv`;
const tempFilePath = path.join(os.tmpdir(), fileName);
const reportRef = db.collection("reports").doc(reportId);
try {
const billsSnapshot = await db.collection("bills").get();
const bills = [];
billsSnapshot.forEach((doc) => {
bills.push({ ...doc.data(), id: doc.id });
});
const preprocessedData = bills.map((item) => {
const newItem = { ...item };
if (newItem.time && newItem.time._seconds) {
// this function converts the timestamp object to time string, ignore if not needed
const dateDelist = new Date(newItem.time._seconds * 1000);
const dateInISTDelist = addMinutes(addHours(dateDelist, 5), 30);
newItem.time = format(dateInISTDelist, "dd-MM-yyyy hh:mm:ss aaa");
}
return newItem;
});
const csv = Papa.unparse(preprocessedData, {
quotes: false,
delimiter: ",",
header: true,
newline: "\r\n",
dynamicTyping: true,
skipEmptyLines: true,
});
await fs.outputFile(tempFilePath, csv);
await bucket.upload(tempFilePath, { destination: fileName });
const file = bucket.file(fileName);
await file.makePublic();
const publicUrl = `https://storage.googleapis.com/${bucket.name}/${fileName}`;
return await reportRef.update({
status: "complete",
downloadLink: publicUrl,
createdAt: admin.firestore.Timestamp.now(),
});
} catch (err) {
return console.log(err);
}
});
Key Points
- Trigger: The function is triggered by creating a new document in the reports collection.
- Data Fetching: Retrieves all documents from the bills collection.
- Date Manipulation: Converts Firestore timestamp fields to a more readable format using date-fns.
- CSV Conversion: Uses Papaparse to convert the data to CSV format.
- File Handling: Creates a temporary file for the CSV, then uploads it to Firebase Storage.
- Public Access: Makes the uploaded file publicly accessible.
- Update Firestore Document: Updates the report document with the CSV file’s download link and marks the report as complete.
- Error Handling: Includes try-catch for robust error management.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we’ve demonstrated how to automate the process of converting Firestore documents into a CSV format using Firebase Cloud Functions. This functionality is particularly useful for generating timely reports or exports, streamlining data management tasks without manual intervention.
Below is a GIF that illustrates how the application behaves once integrated. This visual representation helps to understand the seamless flow from data trigger to CSV generation and retrieval.
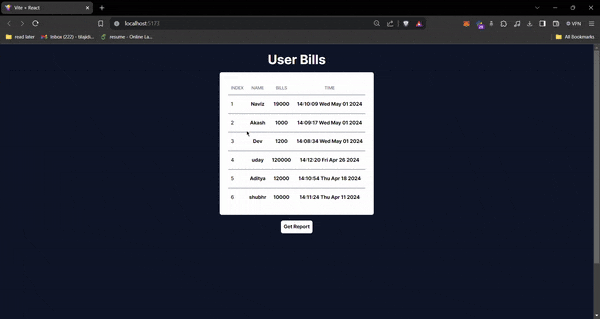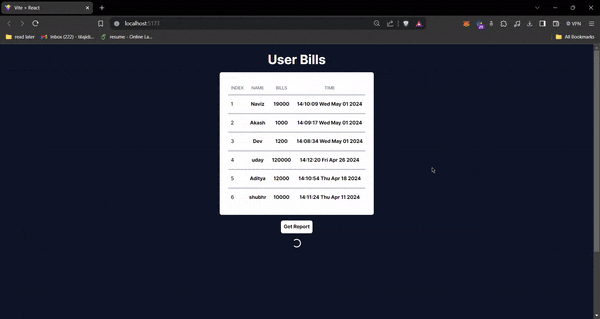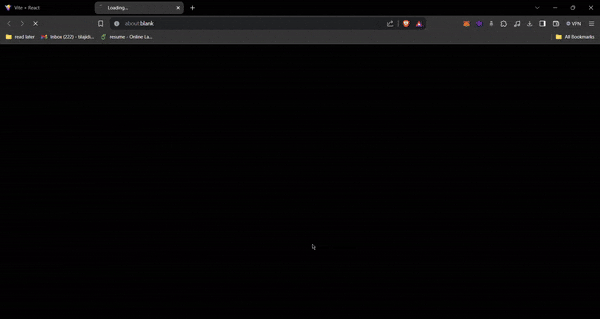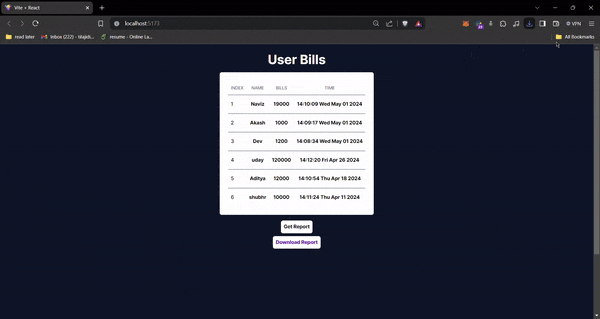
For more detailed code, check out this GitHub repository: https://github.com/dixitt5/firestore-data-to-excel
Happy coding!